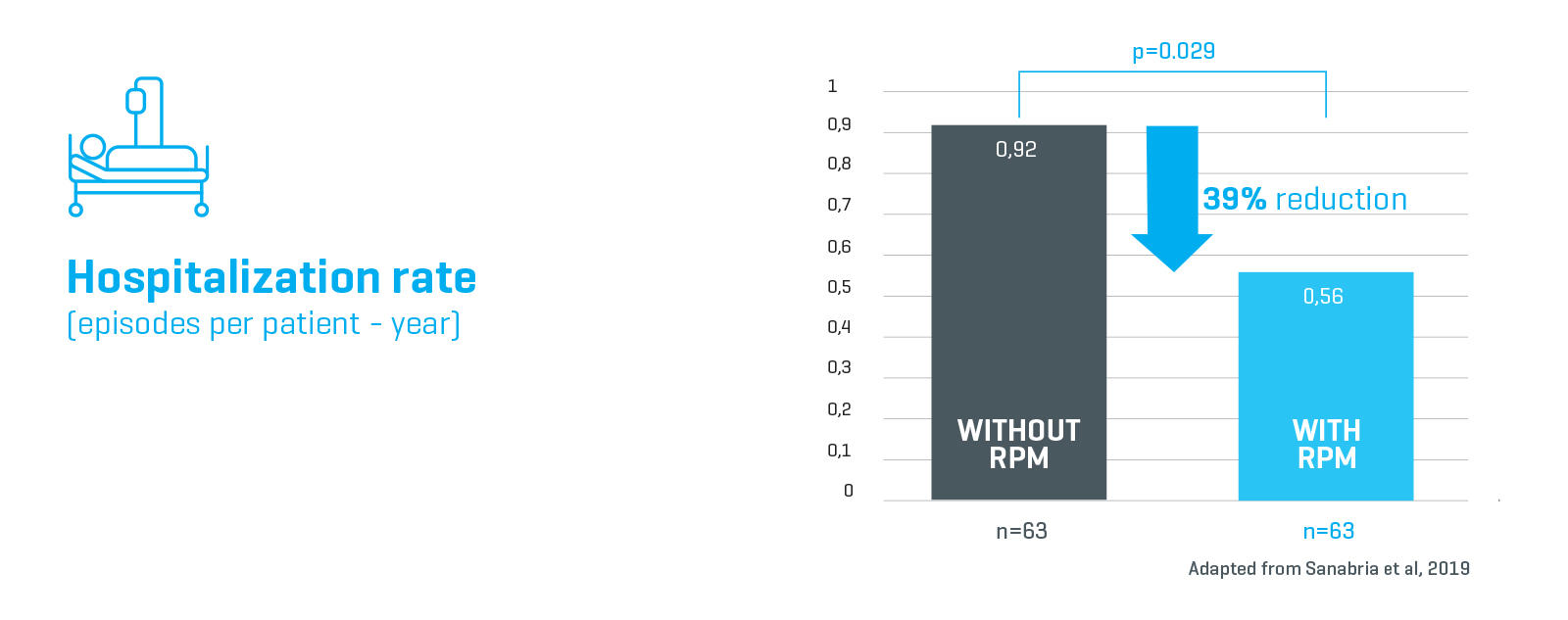
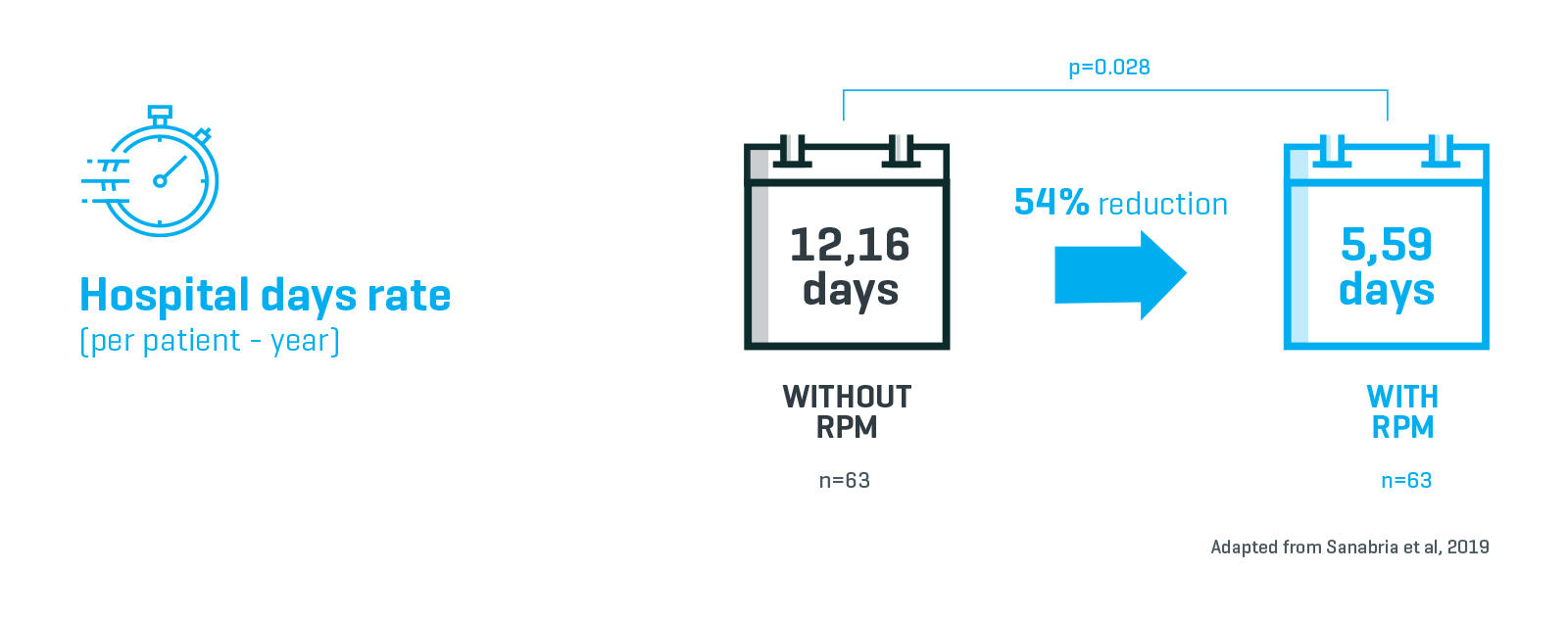
Reduction in rate of hospitalization
Contact MeRemote Patient Management (RPM) enables Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) patients to have their treatment proactively monitored by nurses and clinicians, but without having to spend as much time in the hospital and clinic at the detriment of their care. This may improve treatment adherence and thus reduce risk of complications.
Abstract
Remote management technology specifically designed to be integrated into APD systems may improve adherence to treatment and provide the potential for early intervention should therapy complications be encountered.
Clinical outcomes of incident adult patients treated with APD and RPM were compared to patients treated with APD alone. Patients using APD with RPM had a statistically significant lower rate of hospitalization and duration of stay compared to APD without RPM.

Rationale
The remote management technology, specifically designed to be integrated into APD systems, offers both patients and their clinical team a powerful tool. Via enhanced communication, the tool may improve adherence to treatment and provide the opportunity for early intervention should therapy complications be encountered.
The purpose of this study was to compare the hospitalization rates in incident adult patients on Automated Peritoneal Dialysis with and without Remote Patient Management.
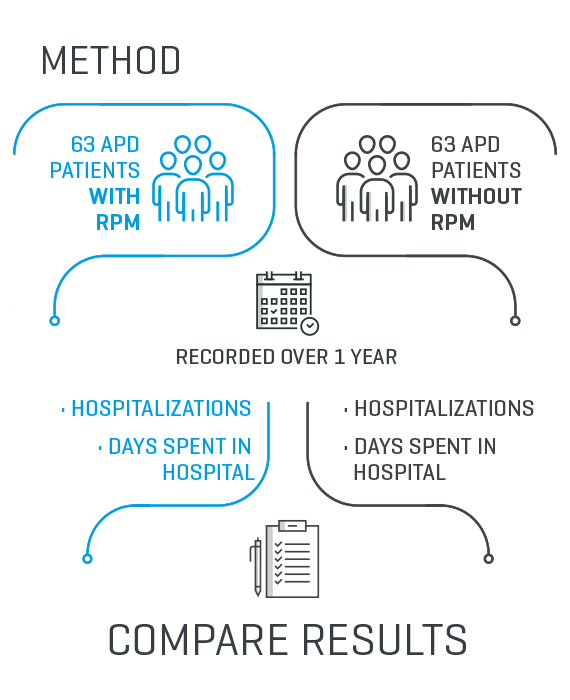
Method
A multicenter retrospective cohort study in incident adult patients performing APD with and without remote monitoring was conducted. Patients were enrolled from October 1, 2016 to June 30, 2017 from 28 renal clinics within the Renal Therapy Service, Columbia network.
Individuals were matched 1:1 using propensity score matching. The APD therapy with RPM and ADP therapy without RPM groups each yielded 63 individuals. Hospitalizations and days spent in hospital were recorded over 1 year.
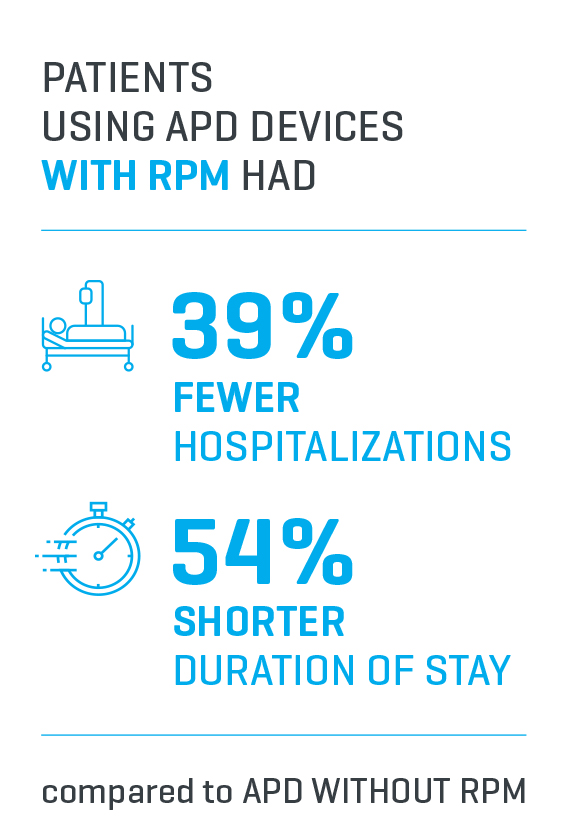
Findings
In the APD with RPM patient group, there was a statistically significant reduction in hospitalizations (39% reduction) and duration of stay (54% fewer days), compared to patients using APD without RPM.1
Implementation of APD cyclers with a remote management program may improve clinical outcomes, such as rate of hospitalization and days spent in hospital.